INTRODUCTION
Business owners and managers have many important decisions to be made on a regular basis, and one of the important areas that they need to look into relates to Financial Management of the business. They need to make the appropriate decisions which must take into consideration the potential impact and consequences that their management decisions will have on the sales, profits, cash flow and the financial position / health of the business and company. The activities of every aspect of a business will undoubtedly have an impact on the company’s financial performance and must be carefully evaluated, managed and controlled by any business owner and manager.
LIFE CYCLE OF BUSINESSES and THE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT CHALLENGES
Typical management textbooks / literature would explain that businesses go through a life cycle, also known as ‘stages of a businesses’. The different stages are as follows:
- Development / Seed Stage
- Start-up Stage
- Growth / Survival Stage.
- Expansion / Rapid Growth Stage.
- Maturity Stage.
These would be explained further in the next write-up.
Financial management challenges
Typically, many businesses / companies experience losses and negative cash flows during the start-up period. Hence, financial management of businesses is extremely important at the stage. Business owners / managers must make sure that there is sufficient cash on hand to meet expenses (in particular the short term, for example the need to be able to pay wages / salaries of employees; settle amounts due to creditors (trade and non-trade); meet the statutory obligations such as the amounts due for EPF / SOCSO / insurance schemes / tax (direct / indirect) and so on. In general, businesses will find there is more cash outflows with very little (or none at all) cash inflows. It is imperative that business owners / managers be able to make financial projections of these negative cash flows so that some forecast of how much capital and initial funding will be needed to fund the business until it becomes profitable and sustainable.
As a business grows and matures, it will need more cash to finance its growth. This is because businesses / companies experience rapid sales growth. When sales rise rapidly, purchases, fixed assets requirements and working capital needs grow exponentially as well. Planning and budgeting for the financial needs at the growth and expansion stage is crucial as customer satisfaction must be assured to ensure survival. Deciding whether to fund expansion through internal funding or to borrow from external parties (including the bank) is an example of a financial management decision made by business owners / managers. Financial management is thus finding the proper source of funds at the lowest cost, controlling the company’s cost of capital and not letting the Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet) become too highly leveraged with debt that will result in adverse effect of its credit rating.
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
Over the long-term and short-term period, businesses and companies undertake various activities and operations to be able to create and/or provide products and/or services, make procurements from creditors, undertake sales and marketing activities, ensure that monies are collected from customers the money and the above-mentioned cycle continuously repeats itself.
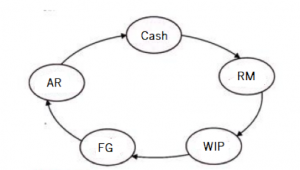
Legend:
RM – Raw Materials
WIP – Work in Progress
FG – Finished Goods
AR – Accounts Receivable
When raw materials are purchased and other supplies / services are procured, businesses may be making such procurements either on cash or credit basis. If the latter scenario comes in, thus Accounts Payable (creditors) are created.
Financial management is moving cash efficiently through this cycle. This means that managing the turnover ratios of raw materials and finished goods inventories, selling to customers and collecting the receivables on a timely basis and starting over by purchasing more raw materials. In the meantime, the businesses / companies must pay its invoices from suppliers (trade and non-trade), employees and statutory obligations. All of this must be done with cash, and it takes astute financial management to make sure that these funds flow efficiently.
Even if the funds are tied up whether in inventory (raw materials, work-in-progress and finished goods) or accounts receivables, there are ways to convert such situations in liquid funds, whether through:
- Working capital borrowings
- Invoice factoring / discounting
- Short term borrowings such as bank overdraft
- Credit card facilities
- Revolving credit and the likes
The abovementioned short-term financing methods will be elaborated further in subsequent articles.
STATUTORY OBLIGATIONS
In general in Malaysia, the statutory obligations of businesses (cash wise) include payments to be made in respect of (limited to obligations by businesses / companies only):
- Employee Provident Fund (EPF) contributions
- Social Security Organisation (SOCSO) contributions
- Employment Insurance Scheme
- Human Resources Development Fund (HRDF) contributions
- Payments to Inland Revenue Board (IRB) in respect of monthly tax instalments and final corporate tax liability, monthly Potongan Cukai Bulanan (monthly tax deduction) of employees
- Payments to Royal Malaysian Customs Department for various types of indirect taxes and so on
Business owners and managers must always plan and ensure that the businesses are able to meet the statutory obligations (some of which are mentioned above) on a timely basis.
SUMMARY
Every small and medium-sized-enterprise will always be driven by the passion and objective of meeting the desired outcome desired by the business owners, mainly to grow and succeed. Accordingly financial management becomes an important skill that every small business owner or manager must acquire and possess. This is owing to the fact that every decision that an owner makes has a financial impact on the business / company, and these decisions must be made within the total context of the business / company’s operations.
Even though economies have a long-term history of being successful, occasionally, businesses will also experience sharp declines (industry and business life cycles). Businesses must plan to have enough liquidity to weather these economic downturns, otherwise they may need to close their doors owing to lack of cash.
Good financial management goes a long way towards ensuring that business resources are available (especially funding requirements) and used efficiently and effectively, and finally, providing optimum returns.
Future articles shall deal with topics such as:
- Stages of business life cycles and the funding requirements
- Types of working capital funding that may be considered
- Factors to consider when deciding on types of financing to be used
- How does invoice financing work? Sources available
- Planning and budgeting and so on
